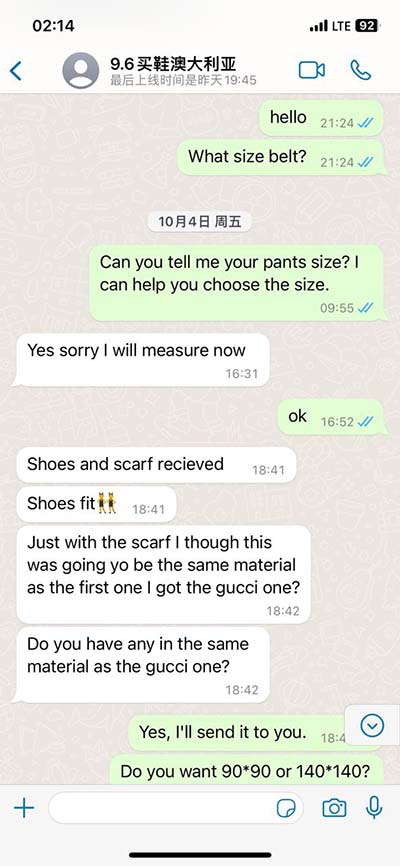
lv pole | 33kv line ground clearance lv pole Radial networksRadial operation is the most widespread and most economic design of both MV and LV networks. It provides a sufficiently high degree of reliability and service continuity for most customers. In American (120 V) systems, the . See more
$55.00
0 · pole mounted circuit breaker
1 · minimum clearance for 33kv
2 · low voltage power supply network
3 · horizontal clearance of 132kv line
4 · distance between 11kv pole to
5 · 33kv line ground clearance
6 · 220 kv clearance requirements
7 · 11kv pole to distance
On sale for $78.20. MSRP $230.00.. 3.0 out of 5 stars. Free shipping BOTH ways on womens superstar adidas shoes from our vast selection of styles. Fast delivery, and .
A low-voltage network or secondary network is a part of electric power distribution which carries electric energy from distribution transformers to electricity meters of end customers. Secondary networks are operated at a low voltage level, which is typically equal to the mains voltage of electric appliances. Most modern . See moreElectric power distribution systems are designed to serve their customers with reliable and high-quality power. The most common distribution system consists of simple radial circuits (feeders) that can be overhead, . See more• Earthing system• Split-phase electric power See more1. ^ Warne 2005, p. 385.2. ^ NREL 2005, p. 1.3. ^ Beaty 1998, p. 84.4. ^ . See more
Most of differences in the layout and design of low-voltage networks are dictated by the mains voltage rating. In Europe and most of . See more
Radial networksRadial operation is the most widespread and most economic design of both MV and LV networks. It provides a sufficiently high degree of reliability and service continuity for most customers. In American (120 V) systems, the . See more
Low-voltage network. A pole-mounted three-phase distribution transformer. Low-voltage feeders distributing power to households are placed below the transformer. A low-voltage network or .

The LV, Low Voltage, pole is a tier 1 machine used to transfer electricity across medium to long distances. The pole has two nodes that can separately receive and send electricity from and to . Electrical safety standards for LV/MV/HV includes water safely clearance on electrical fires, minimum approach distance for authorized and ordinary
Where more than one substation supplies a village, arrangements are made at poles on which the LV lines from different substations meet, to interconnect corresponding . 1. Simple Low Voltage Radial System. In a conventional low-voltage radial system, the utility owns the pole-mounted or pad-mounted transformers that step their distribution .
Low Voltage (LV) Distribution System. Most European countries use 230/400 V for low voltage (LV) distribution, or in some cases 240/415 V instead. The majority of residential customers .
Electrical design engineers must adhere to contemporary standards for substation and power distribution in buildings. For example, in some past times, numerous countries . Low voltage (LV) cable systems up to 1 kV serve to connect buildings and carry power over short distances of not more than several hundred meters. A transformer connects . An insight, background on the main character and topologies of the LV networks with highlighting the key differences between LV networks and both high-voltage (HV) and .
LV Pole accessories. Selection of accessories such as supporting stay wire sets, pole base reinforcers, pole hats and bolts. A variety of standardized sets available for these purposes .Low-voltage network. A pole-mounted three-phase distribution transformer. Low-voltage feeders distributing power to households are placed below the transformer. A low-voltage network or .The LV, Low Voltage, pole is a tier 1 machine used to transfer electricity across medium to long distances. The pole has two nodes that can separately receive and send electricity from and to .
Electrical safety standards for LV/MV/HV includes water safely clearance on electrical fires, minimum approach distance for authorized and ordinary Where more than one substation supplies a village, arrangements are made at poles on which the LV lines from different substations meet, to interconnect corresponding . 1. Simple Low Voltage Radial System. In a conventional low-voltage radial system, the utility owns the pole-mounted or pad-mounted transformers that step their distribution .Low Voltage (LV) Distribution System. Most European countries use 230/400 V for low voltage (LV) distribution, or in some cases 240/415 V instead. The majority of residential customers .
Electrical design engineers must adhere to contemporary standards for substation and power distribution in buildings. For example, in some past times, numerous countries . Low voltage (LV) cable systems up to 1 kV serve to connect buildings and carry power over short distances of not more than several hundred meters. A transformer connects . An insight, background on the main character and topologies of the LV networks with highlighting the key differences between LV networks and both high-voltage (HV) and .
givenchy iphone x case price
179K subscribers in the adidas community. A subreddit for discussion, images, videos, and everything related to adidas.
lv pole|33kv line ground clearance