lv trabeculation and false cord | excessive trabeculation of left ventricle lv trabeculation and false cord Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or . mixing mercon lv and mercon sp in the torqshift transmission is acceptable. USE MERCON LV TRANSMISSION FLUID TO SERVICE VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH TORQSHIFT TRANSMISSIONS. WHEN ADDING OR REPLACING TRANSMISSION FLUID IN A VEHICLE EQUIPPED WITH A TORQSHIFT .
0 · pathophysiology of trabeculation
1 · left ventricular trabeculation
2 · left ventricle trabecular
3 · excessive ventricular trabeculation
4 · excessive trabeculation of left ventricle
10 votes, 139 comments. Posted in the u_Budget-Ad3877 community.
Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, .Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, .Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to . Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or .
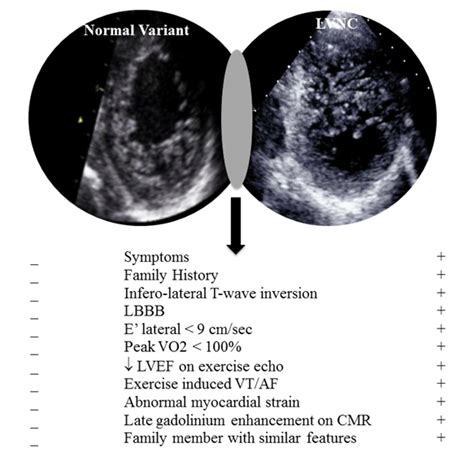
Patients with LVNC frequently (75%) express symptoms of LV dysfunction whereas athletes are asymptomatic. These individuals also frequently (66%) demonstrate a .First of all, the proper identification of left ventricular structures such as LV thrombus, false tendons, aberrant chords, cardiac fibromas, eosinophilic heart disease, endomyocardial .Arrows indicate the location of left ventricular false tendon, a single chord (simple type) traversing the left ventricular cavity from the basal to the apical zone (longitudinal type) measuring 1.4 .In normal human hearts the left ventricle (LV) has up to 3 prominent trabeculations and is, thus, less trabeculated than the right ventricle. Rarely, more than 3 prominent trabeculations can be .
Incidence and characteristics of left ventricular false tendons and trabeculations in the normal and pathologic heart by second harmonic echocardiographyIn multivariate analysis, LV dilation and presence of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) were the only significant independent CMR predictors of adverse outcomes. In fact, none of the event .Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, acquired, developmental, or congenital origins.
Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, acquired, developmental, or congenital origins.Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to the mitral valve apparatus, the term “false” tendon is in use. Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or to the free wall of the ventricle but not to the mitral valve. They are found in approximately half .
Patients with LVNC frequently (75%) express symptoms of LV dysfunction whereas athletes are asymptomatic. These individuals also frequently (66%) demonstrate a LV cavity >64 mm, an ejection fraction <45%, suppressed longitudinal LV function (Sa <9 cm/sec), and impaired LV filling (E' <9 cm/sec).First of all, the proper identification of left ventricular structures such as LV thrombus, false tendons, aberrant chords, cardiac fibromas, eosinophilic heart disease, endomyocardial fibrosis, and cardiac metastasis, which can imitate LVNC, should be performed.Arrows indicate the location of left ventricular false tendon, a single chord (simple type) traversing the left ventricular cavity from the basal to the apical zone (longitudinal type) measuring 1.4 mm in thickness (thin type).In normal human hearts the left ventricle (LV) has up to 3 prominent trabeculations and is, thus, less trabeculated than the right ventricle. Rarely, more than 3 prominent trabeculations can be found at autopsy and by various imaging techniques in the LV.

pathophysiology of trabeculation
Incidence and characteristics of left ventricular false tendons and trabeculations in the normal and pathologic heart by second harmonic echocardiographyIn multivariate analysis, LV dilation and presence of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) were the only significant independent CMR predictors of adverse outcomes. In fact, none of the event-free patients had abnormal LV volumes or LGE. These findings have important clinical implications.Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, acquired, developmental, or congenital origins.Excessive trabeculation is frequently observed by imaging studies in healthy individuals, as well as in association with pregnancy, athletic activity, and with cardiac diseases of inherited, acquired, developmental, or congenital origins.
Left ventricular false tendons (LVFTs) are echogenic fibromuscular structures, connecting the left ventricular free wall or papillary muscle and the ventricular septum. As they are not related to the mitral valve apparatus, the term “false” tendon is in use.
Left ventricular (LV) false tendons are chordlike structures that traverse the LV cavity. They attach to the septum, to the papillary muscles, or to the free wall of the ventricle but not to the mitral valve. They are found in approximately half .
Patients with LVNC frequently (75%) express symptoms of LV dysfunction whereas athletes are asymptomatic. These individuals also frequently (66%) demonstrate a LV cavity >64 mm, an ejection fraction <45%, suppressed longitudinal LV function (Sa <9 cm/sec), and impaired LV filling (E' <9 cm/sec).First of all, the proper identification of left ventricular structures such as LV thrombus, false tendons, aberrant chords, cardiac fibromas, eosinophilic heart disease, endomyocardial fibrosis, and cardiac metastasis, which can imitate LVNC, should be performed.
Arrows indicate the location of left ventricular false tendon, a single chord (simple type) traversing the left ventricular cavity from the basal to the apical zone (longitudinal type) measuring 1.4 mm in thickness (thin type).In normal human hearts the left ventricle (LV) has up to 3 prominent trabeculations and is, thus, less trabeculated than the right ventricle. Rarely, more than 3 prominent trabeculations can be found at autopsy and by various imaging techniques in the LV.
Incidence and characteristics of left ventricular false tendons and trabeculations in the normal and pathologic heart by second harmonic echocardiography

chanel chance sample vial

left ventricular trabeculation
ct. A retrospective cardiac gated CTA with calcium score confirmed a large calcified lesion at LV apex. It is most likely a calcified thrombus. No obvious apical aneurysm was seen, Case Discussion. The patient did not have a known history of coronary artery disease (CAD) but was at high risk for CAD due to the history of tobacco and drug use.
lv trabeculation and false cord|excessive trabeculation of left ventricle