lv i kwv | Understanding LVH Part 2: How to Mea lv i kwv Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST . 1 personas están hablando de esto
0 · Understanding LVH Part 2: How to Mea
1 · THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ECHOC
2 · Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
3 · Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LIT
4 · Left Ventricular Diastolic Function
5 · Echocardiographic Assessment of Left V
Savukārt, vērtējot finansiālo ieguvumu, izmaksu ietaupījums pēc renovācijas ir 5.8 eiro uz katru kvadrātmetru. Pēc veiktajiem atjaunošanas pasākumiem ēka ieguvusi B energoklasi. Projekta pirms un pēc foto pieejami failiem.lv/u/t73hbp436g. Ietaupījums 71% – māja Vecumniekos, Rīgas ielā 33. Ēkā veikta pagraba pārseguma .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST .RWPT in wide QRS complex tachycardia. R-wave peak time (RWPT) may be .ECG Pearl. There are no universally accepted criteria for diagnosing RVH in .ECG Criteria for Left Atrial Enlargement. LAE produces a broad, bifid P wave in .
In LBBB, conduction delay means that impulses travel first via the right bundle .
References. Sovari AA, Farokhi F, Kocheril AG. Inverted U wave, a specific .
Left Axis Deviation = QRS axis less than -30°.. Normal Axis = QRS axis between .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.Significance: Impaired (slow) early left ventricular relaxation. Signs and symptoms: None at rest. Functional status: Mild impairment. Left atrium: Normal dimension (may be hypercontractile) Filling pressures: Normal. PW Doppler findings: E/A ratio < 1.0. Deceleration time > 240 msec. IVRT > 90 msec.
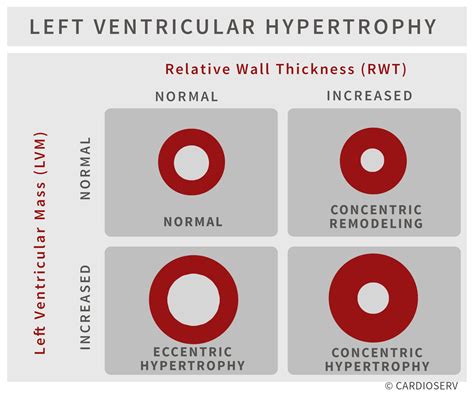
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .LVM and RWT. LVM is the acronym for Left Ventricular Mass. LV mass (LVM) is a vital prognostic measurement we obtain with echocardiography to manage hypertension. RWT is the acronym for Relative Wall Thickness and is an additional reference value that can help further classify the .
(see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF Volumes can be derived from 2DE or 3DE (see section on LV size for methodology).
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging (eg, echocardiography, cardiovascular computed tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance [CMR] imaging) [1].Left ventricular function correlates strongly with total and cardiovascular mortality (Curtis et al). Among patients with coronary heart disease, left ventricular function is actually a stronger predictor of death than the atherosclerotic burden.Ejection fraction is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume (EDV, i.e blood volume in the ventricle at the end of diastole) that is pumped out during systole. Currently, two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography for calculation of ejection fraction is the dominant method for assessing left ventricular function (systolic function).
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.Left Ventricular Function. Myocardial Mechanics: Structure and Function of Myocardial Fibers. Ventricular Pressure-Volume Relationship: Preload, Afterload, Stroke Volume, Wall Stress & Frank-Starling’s law. Assessing left ventricular systolic function. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.
Significance: Impaired (slow) early left ventricular relaxation. Signs and symptoms: None at rest. Functional status: Mild impairment. Left atrium: Normal dimension (may be hypercontractile) Filling pressures: Normal. PW Doppler findings: E/A ratio < 1.0. Deceleration time > 240 msec. IVRT > 90 msec.Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .LVM and RWT. LVM is the acronym for Left Ventricular Mass. LV mass (LVM) is a vital prognostic measurement we obtain with echocardiography to manage hypertension. RWT is the acronym for Relative Wall Thickness and is an additional reference value that can help further classify the .(see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF Volumes can be derived from 2DE or 3DE (see section on LV size for methodology).
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a common finding in patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD risk factors and is diagnosed either by electrocardiogram (ECG) or imaging (eg, echocardiography, cardiovascular computed tomography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance [CMR] imaging) [1].Left ventricular function correlates strongly with total and cardiovascular mortality (Curtis et al). Among patients with coronary heart disease, left ventricular function is actually a stronger predictor of death than the atherosclerotic burden.Ejection fraction is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume (EDV, i.e blood volume in the ventricle at the end of diastole) that is pumped out during systole. Currently, two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography for calculation of ejection fraction is the dominant method for assessing left ventricular function (systolic function). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.
prada wallet ราคา
© 2021 ENCOUNTER CHURCH VEGAS. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. 237 N Stephanie St. Suite E , Henderson, NV 89074 Office Phone: (702) 293-6777 Email:[email protected]
lv i kwv|Understanding LVH Part 2: How to Mea